Inflation is one of the most important global topics of 2022, with the U.S. hitting 8.3%, the UK as high as 10.1%, and countries such as Turkey seeing figures as high as 79.6%. These figures are well beyond the target rate of 2% inflation by the major central banks.
Central banks such as the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, and Bank of England aim to keep inflation low and stable. An inflation target of 2% helps everyone plan for the future. If inflation is too high or it moves around a lot, it’s hard for businesses to set the correct prices and for people to plan their spending.
What is the impact of 2% inflation?
To understand the impact of inflation, you need to look at the compound impact over a series of years. Suppose you have $50,000 in your savings account; at 2% inflation compounding annually over 20 years, your spending power will have reduced to just $33,648. Your savings will effectively be reduced by almost $17,000 by just sitting in the bank.
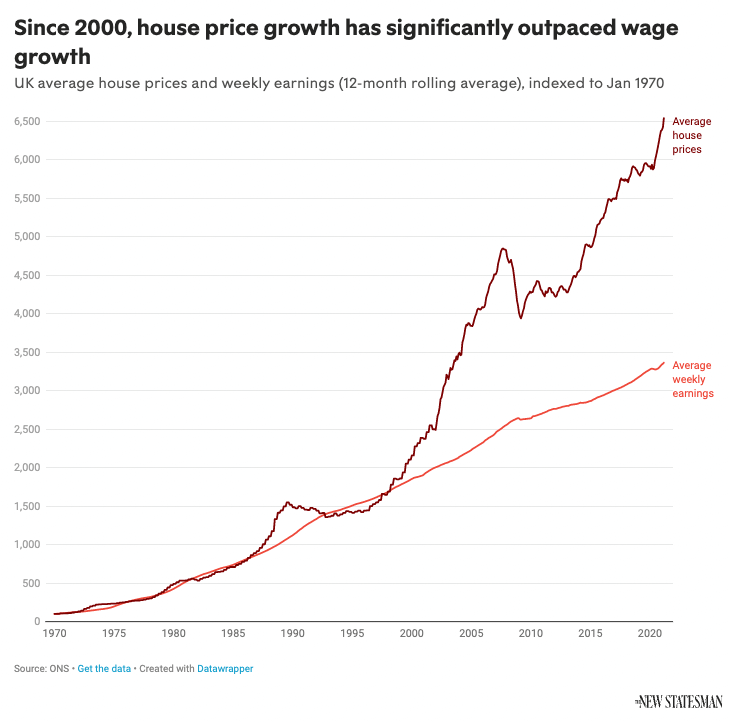
If wages increase by the exact figure of 2% per year, then this is balanced out. However, historically this is not the case.. The average home price in the UK has drastically outpaced average earnings growth. Therefore, since around the turn of the millennium, it has become increasingly difficult for the average worker to save to buy their own home.
Dealing with inflation
Central banks are expected to eventually get inflation under control using tools they have at their disposal. There has been high inflation in the past, so it is not unreasonable to assume that similar methods will be implemented in 2022 to reduce inflation based on past successes.
Historically, to deal with inflation anytime it has risen above 5%, the Federal Reserve has increased the federal funds rate to exceed the level of CPI inflation. The red arrows on the chart below indicate this has been implemented six times in the past 20 years.
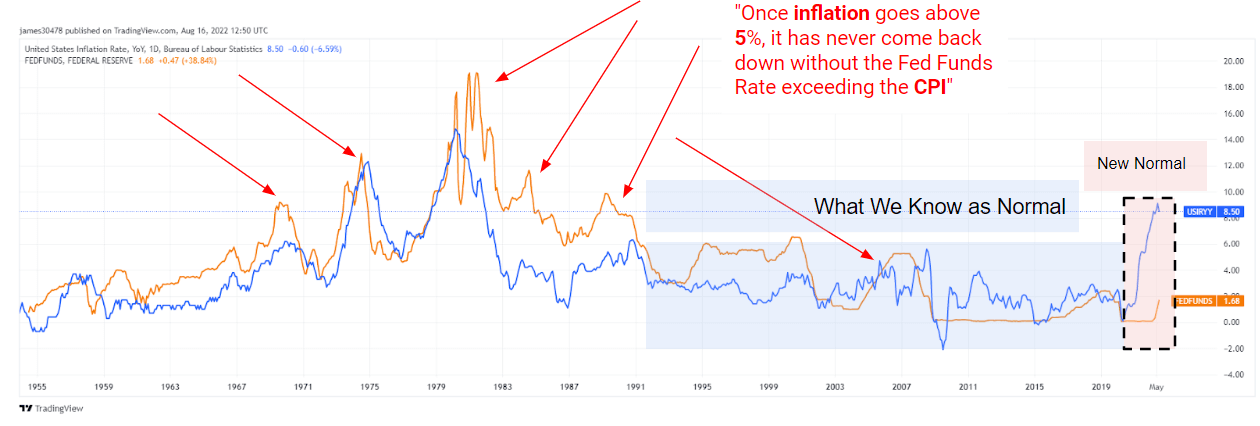
For the best part of the last 20 years, CPI inflation has averaged around the goal of 2%. In 2022, there is talk of a “new normal.” Never has there been a more significant disconnect between CPI and FED funds rate with inflation so far above interest rates.
The strategy to combat inflation spikes similar to those currently affecting global markets has also been to increase interest rates beyond that of inflation.
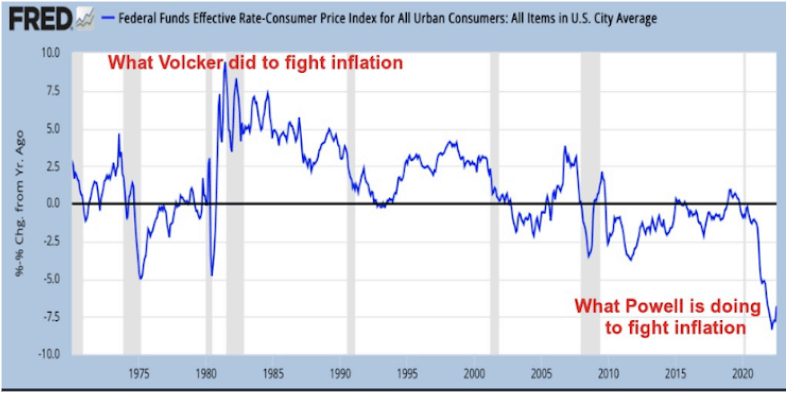
In the 1970s, when CPI inflation was in the double digits, Paul Volcker, FED chair at the time, managed to get the FED funds rate over 12%. However, the actions of the current FED chairman, Jerome Powell, are worlds apart from Volcker’s. The chart below illustrates the relationship between the FED funds rates and CPI inflation since 1970. Volcker facilitated an over 7.5% YoY change, while Powell has had the opposite effect with a negative 7.5% change.
Crypto inflation
Bitcoin can be viewed as an asset to protect yourself from currency debasement, but it does have inflation of its own. The inflation of Bitcoin is programmed into the protocol. At present, Bitcoin’s inflation rate is 1.75%; however, in 2024, it will reduce to 0.875%, and it will continue to decrease following each halving event.
The only slight variance in the inflation rate for Bitcoin relates to the hashpower of the network relative to the network difficulty. If there is a change in the hashrate, it is automatically adjusted by increasing or decreasing the network difficulty to control inflation.
Bitcoin’s inflation model aims to gradually reduce it over time rather than maintain inflation at a set rate. The tools to control inflation are programmed into the protocol, so there is no need for a central bank or other governing body to make any decisions to get inflation under control.
Further, Ethereum is going through a significant change in its inflation rates this year. Before The Merge, Ethereum’s inflation rate is roughly 2.6%. This was cut in half after the implementation of EIP-1559 in 2021.
EIP-1559 has cut the ETH yearly inflation rate from 4.2% to 2.6%.
Once the merge happens in a few months and PoS is live, this will be a negative number.
Ethereum will be secure while ETH deflationary. The best crypto monetary policy that exists.
— eric.eth (@econoar) August 7, 2021
After The Merge, the issuance will be drastically reduced, potentially resulting in a negative inflation rate below 0%, with ETH issuance around 0.3%. The change results from the triple halving that will take place as the 13k ETH daily miner rewards are removed, leaving just the 1.3K ETH from staking.
Lucas Outumuro from Into the Block projected that it could go as low as -4.5% when considering network fees.
$ETH will become deflationary following the merge
ETH’s net issuance is likely to range between -0.5% to -4.5% depending on network fees
Here is a projection of what that would look like based on 2022 historical data pic.twitter.com/KdWq072Mbz
— Lucas (@LucasOutumuro) July 22, 2022
Bitcoin and Ethereum were created after the 2008 recession to respond to the problems that have plagued the traditional banking system for years. Neither protocol aims to keep inflation at a number close to 2%. Both networks reduce inflation over time, increasing the underlying assets’ buying power. A negative inflation rate means holding Bitcoin or Ethereum will make it worth more in real terms over a long enough timeframe.
Unlike holding fiat currencies which, even at the central banks’ target inflation rate, will fall in buying power, Bitcoin and Ethereum are programmed to do quite the opposite. Fiat inflation rates are, while slowing, still rising globally. Yet, Ethereum will undergo an upgrade in September, causing one of the largest deflationary events in history. How this will affect speculation on the price of Ethereum will be very interesting to watch.
It is important to note that economics is not as simple as “inflation bad, deflation good.” In fact, there are many consequences of deflation that can be harmful to the economy. The goal of a 2% inflationary target is to ensure that the velocity of money continues at a healthy rate.
If there is 0% or negative inflation, then it is wise to refrain from spending. Holding on to an asset with negative inflation means it will be worth more over time, so you are losing out on future spending power by spending it now. This trend can cause an economy to grind to a halt as the velocity of money falls. Therefore, the central banks set a low inflationary target to ensure spending continues.
However, as the example at the start of this article illustrated, even 2% inflation drastically reduces your savings over 20 years. Ethereum and Bitcoin have lower inflation rates while also being programmed by global community consensus.
There is no central bank for Bitcoin or Ethereum and, therefore, no chairperson to misjudge the handling of the economy. The economy is already decided and baked into the code. If the goal of 2% inflation is to ensure people can plan their future, what better way than to have the next 100 years set out in front of you, as is the case with Bitcoin?



