The U.S. nationwide debt reached its all-time excessive this month, surpassing $31 trillion.
Over $11 trillion of the debt was added previously 10 years alone, $5 trillion of which was a direct results of the debt spending initiated by the Biden administration in 2020.
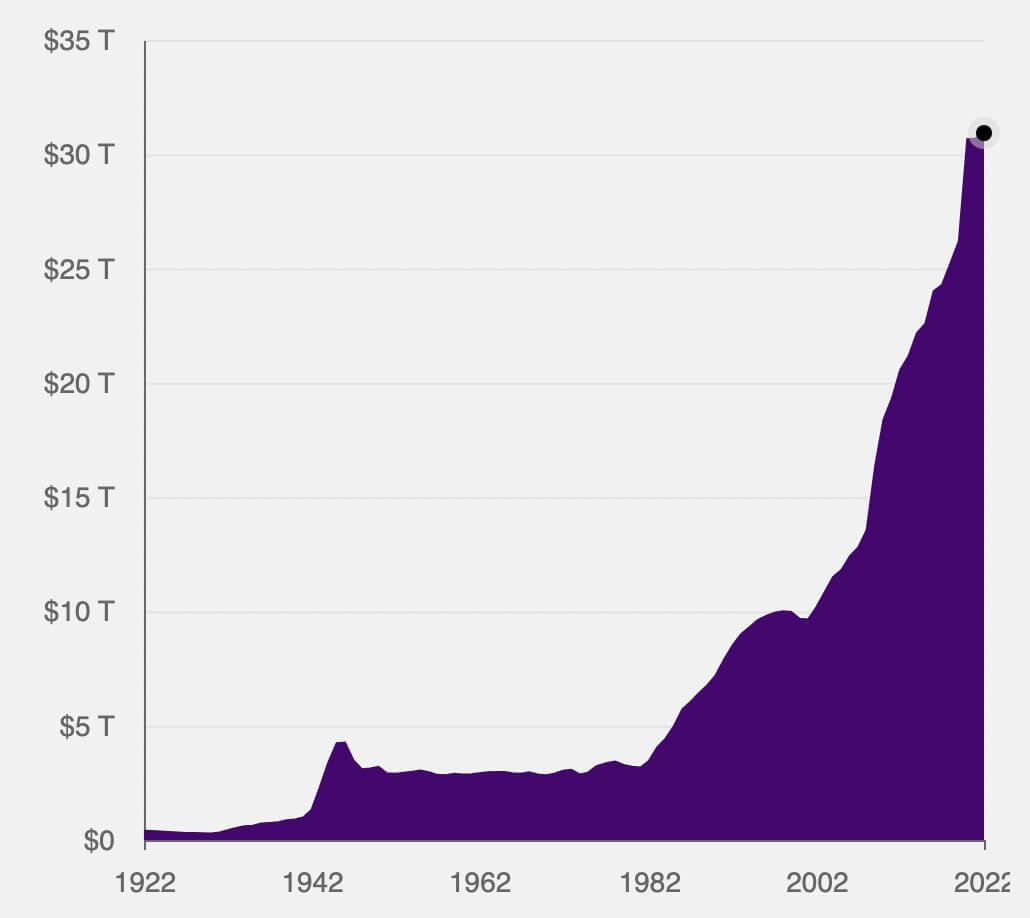
In line with The Committee for a Accountable Federal Price range, the $5 trillion consists of President Biden’s signature $1.9 trillion stimulus invoice, a number of new congressionally-approved spending initiatives, and a student-loan debt forgiveness plan anticipated to price practically $400 billion.
Whereas many economists argue {that a} sure stage of debt is critical to stimulate progress, the present nationwide debt breaks all beforehand seen thresholds. The world’s main financial system is working a deficit, with the ratio of debt to GDP at the moment standing at 137%. The $31 trillion the U.S. owes dwarfs the $25 trillion GDP it noticed this 12 months.
Regardless of the federal government’s efforts to scale back the deficit for the 2022 fiscal 12 months, economists anticipate it’s going to rise increased than beforehand anticipated over the following three years. That is largely as a consequence of rising charges driving increased curiosity prices, which many consider will additional improve the nationwide debt.
As important chunks of the debt mature, they are going to have to be changed with further borrowing, with rates of interest compounding. Changing the $31 trillion of debt at a 3.2% fee would carry the rate of interest expense to $1 trillion yearly.
Present financial situations imply that the U.S. would wish to borrow more cash to repay rates of interest. With authorities spending quickly outpacing tax income, the deficit will proceed to extend. A declining financial system heading right into a recession has already dealt heavy blows to the market, wiping out billions in revenue. The losses retail traders undergo imply fewer capital positive aspects taxes, whereas the losses institutional traders undergo cut back the general quantity of company taxes the federal government collects.
Regardless of the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbating the difficulty, this drawback started lengthy earlier than 2020. The rising debt has been hanging over the U.S. financial system for the reason that late Nineteen Nineties and exploded in 2007 with the onset of the Nice Monetary Disaster. Resolving the wreckage left by over-leveraged monetary establishments required aggressive quantitative easing (QE), setting a strong basis for an additional recession.




